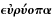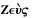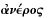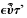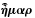"Why increase the sons of Africa, by planting them in America, where we have so fair an opportunity, by excluding all blacks and tawnys, of increasing the lovely white and red?" - Benjamin Franklin's (America as a Land of Opportunity, 1751)
*****************************************
NOTES TO READERS: Colored and/or underlined words are HTML links. Click on them to see the linked posts/articles. Forwarding this and other posts to relatives and friends, especially those in the homeland, is greatly appreciated. To share, use all social media tools: email, blog, Google+, Tumblr,Twitter,Facebook, etc. THANKS!!
Click the following underlined title/link to checkout these Essential/Primary Readings About Us Filipino Natives:
****************************************
Hi All,
I borrow a direct definition of "racism" here according to the Dictionary of Social Sciences (1964): "the doctrine that there is a connection between racial and cultural traits, and that some races are inherently superior to others."
Racism has been intrinsic to America since its colonial beginnings. It was inherited from the first European settlers, who had deeply rooted racist attitudes. In the midst of an allegedly democratic society, it flourished; and its style and rhetoric evolved from being blatantly overt to more subtle and discreet forms as especially characteristic in America today.
Racism has exhibited its deadly consequences: as we have seen in recent generations, or /years or months, i.e. abroad in America’s Humanitarian Wars (interventions): Philippine Invasion/Colonization, Vietnam, Afghanistan and Iraq to name a few; and domestic, lynching, etc. and in recent weeks, murderous shootings of members of non-white religious sects and/or cultural groupings.
America's literature of hatred testifies to this paradox. The hostility contained in the defense of Black Slavery (with the systematic presentation of Blacks as subhuman -include us native Filipinos during the American invasion and so-called Pacification of the Philippines ), the anti-Indian literature of the 19th century, the fear of the "yellow peril," and the influential assertions of ethnic superiority by many leading advocates that include America's Founding Fathers Benjamin Franklin, Thomas Jefferson and Alexander Hamilton.
I have touched on Jefferson's racism in a previous post, click to read -->http://www.thefilipinomind.com/2012/01/thomas-jefferson-and-negro-inferiority.html
Below is a sample of such an assertion from Benjamin Franklin.
- Bert
*******************************************
BENJAMIN FRANKLIN AND AMERICAN RACISM
Title: America as a Land of Opportunity
Author: Benjamin Franklin
Year: 1751
Type of document: essay
Quotation: "Why increase the Sons of Africa...where we have so fair an Opportunity...of increasing the lovely White and Red?"
Annotation:
Perhaps the most important essay written by an American during the eighteenth century, Franklin's "Observations Concerning the Increase of mankind" was one of the first serious studies of demography.
In the early nineteenth century it would serve as an inspiration for Thomas Robert Malthus (1766-1834), who based his grim law of population (that population would inevitably outstrip the food supply) on Franklin's calculations.
But Franklin's argument was, in fact, quite different from Malthus's bleak prophesy. Franklin, like other Americans as late as Lincoln, held to a belief that no man in America needed to long remain a laborer for others. Despite the doubling of the population in every twenty years or so, America remained a land of opportunity, where wages remained high and even slaves were expensive.
In the early nineteenth century it would serve as an inspiration for Thomas Robert Malthus (1766-1834), who based his grim law of population (that population would inevitably outstrip the food supply) on Franklin's calculations.
But Franklin's argument was, in fact, quite different from Malthus's bleak prophesy. Franklin, like other Americans as late as Lincoln, held to a belief that no man in America needed to long remain a laborer for others. Despite the doubling of the population in every twenty years or so, America remained a land of opportunity, where wages remained high and even slaves were expensive.
What is perhaps most striking about Franklin's essay today is his sophisticated use of "social science" data to convince the British ministry to alter its colonial policies. Particularly jarring, however, is Franklin's plea that America be maintained as an entirely Anglo-Saxon society.
Full Text:
Europe is generally full settled with Husbandmen, Manufacturers, &c. and therefore cannot now much increase in People: America is chiefly occupied by Indians, who subsist mostly by Hunting. But as the Hunter, of all Men, requires the greatest Quantity of Land from whence to draw his Subsistence, (the Husbandman subsisting on much less, the Gardner on still less, and the Manufacturer requiring the least of all), The Europeans found America as fully settled as it well could bee by Hunters; yet these having large Tracks, were easily prevail'd on to part with Portions of Territory to the new Comers, who did not much interfere with the Natives in Hunting, and furnish'd them with many Things they wanted.
Land being thus plenty in America, and so cheap as that a labouring Man, that understands Husbandry, can in a short Time save Money enough to purchase a Piece of new Land sufficient for a Plantation, whereon he may subsist a Family; such are not afraid to marry; for if they even look far enough forward to consider how their Children when grown up are to be provided for, they see that more Land is to be had at Rates equally easy, all Circumstances considered.
Hence Marriages in America are more general, and more generally early, than in Europe. And if it is reckoned there, that there is but one Marriage per Annum among 100 Persons, perhaps we may here reckon two; and if in Europe they have but 4 Births to a Marriage (many of their Marriages being late) we may here reckon 8, of which if one half grow up, and our Marriages are made, reckoning one with another at 20 Years of Age, our People must at least be doubled every 20 Years.
But notwithstanding this Increase, so vast is the Territory of North-America, that it will require many Ages to settle it fully; and till it is fully settled, Labour will never be cheap here, where no Man continues long a Labourer for others, but gets a Plantation of his own, no Man continues long a Journeyman to a Trade but goes among those new Settlers, and set up for himself, &c. Hence Labour is no cheaper now, in Pennsylvania, than it was 30 Years ago, tho' so many Thousand labouring People have been imported.
The Danger therefore of these Colonies interfering with their Mother Country in Trades that depend on Labour, Manufactures, &c. is too remote to require the Attention of Great-Britain.
But in Proportion to the Increase of the Colonies, a vast Demand is growing for British Manufacturers, a glorious Market wholly in the Power of Britain, in which Foreigners cannot interfere, which will increase in a short Time even beyond her Power of supplying, tho' her whole Trade should be to her Colonies: Therefore Britain should not too much restrain Manufactures in her Colonies. A wise and good Mother will not do it. To distress, is to weaken, and weakening the Children, weakens the whole Family....
'Tis an ill-grounded Opinion that by the Labour of Slaves, America may possibly vie in Cheapness of Manufactures with Britain. The Labour of Slaves can never be so cheap here as the Labour of working Men is in Britain. Any one may compute it. Interest of Money in the Colonies from 6 to 10 per Cent. Slaves one with another cost L30 Sterling per Head. Reckon then the Interest of the first Purchase of a Slave, the Insurance or Risque on his life, his Clothing and Diet, Expences in his Sickness and Loss of Time, Loss by his Neglect of Business (Neglect is natural to the Man who is not to be benefitted by his own Care or Diligence), Expense of a Driver to keep him at Work, and his Pilfering from Time to Time, almost every Slave being by Nature a Thief, and compare the whole Amount with the Wages of a Manufacturer of Iron or Wool in England, you will see that Labour is much cheaper there than it can ever be by Negroes here. Why then will Americans purchase Slaves? Because Slaves may be kept as long as a Man pleases, or has Occasion for their Labour; while hired Men are continually leaving their Master (often in the midst of his Business) and setting up for themselves.
....There are suppos'd to be now upwards of One Million English Souls in North-America, (tho' 'tis thought scarce 80,000 have been brought over Sea) and yet perhaps there is not one the fewer in Britain, but rather more, on Account of the Employment the Colonies afford to Manufacturers at Home. This Million doubling, suppose but once in 25 Years, will in another Century be more than the People of England, and the greatest Number of Englishmen will be on this Side the Water. What an Accession of Power to the British Empire by Sea as well as Land! What Increase of Trade and Navigation! What Number of Ships and Seamen! We have been here but little more than 100 Years, and yet the Force of our Privateers in the late War, united, was greater, both in Men and Guns, than that of the whole British Navy in Queen Elizabeth's Time....
And since Detachments of English from Britain sent to America, will have their Places at Home so soon supply'd and increase so largely here; why should the Palatine Boors [Germans] be suffered to swarm into our Settlements, and by herding together establish their Language and Manners to the Exclusion of ours? Why should Pennsylvania, founded by the English, become a Colony of Aliens, who will shortly be so numerous as to Germanize us instead of our Anglifying them, and will never adopt our Language or Customs, any more than they can acquire our Complexion.
Which leads me to add one Remark: That the Number of purely white People in the World is proportionably very small. All Africa is black or tawny. Asia chiefly tawny. America (exclusive of the new Comers) wholly so. And in Europe, the Spaniards, Italians, French, Russians and Swedes, are generally of what we call a swarthy Complexion; as are the Germans also, the Saxons only excepted, who with the English, make the principal Body of White People on the Face of the Earth. I could wish their Numbers were increased.
And while we are, as I may call it, Scouring our Planet, by clearing America of Woods, and so making this Side of our Globe reflect a brighter Light to the Eyes of Inhabitants in Mars or Venus, why should we in the Sight of Superior Beings, darken its People? why increase the Sons of Africa, by Planting them in America, where we have so fair an Opportunity, by excluding all Blacks and Tawneys, of increasing the lovely White and Red? But perhaps I am partial to the complexion of my Country, for such Kind of Partiality is natural to Mankind.
"History and observation both teach that....the Mongol, the Malay, the Indian, and the Negro, are now and have been in all ages and places inferior to the Caucasian." - Joseph C. Nott (1844)
***********************************************************
PLEASE DONATE CORE SUBJECT BOOKS TO OUR HOMELAND (i.e. your hometown public schools, alma mater, etc.). Those books that you and/or your children do not need or want; or buy books from your local library during its cheap Book Sales. It is a small sacrifice. Also, cargo/door-to-door shipment is best.
***********************************************************
I consider the following previous posts and the RECTO READER are essential about our homeland and us native, Malay Filipinos; and are therefore always presented in each new post. Click each to open/read.
- WHAT WE FILIPINOS SHOULD KNOW:
- WHAT IS NATIONALISM [Filipino Nationalism]?
- Our Colonial Mentality and Its Roots
- The Miseducation of the Filipino (Formation of our Americanized Mind)
- Jose Rizal - Reformist or Revolutionary?
- The Purpose of Our Past, Why Study (Our) History?
- Studying and Rethinking Our Philippine History
- Globalization (Neoliberalism) – The Road to Perdition in Our Homeland
- Resisting Globalization (WTO Agreements)
- Virtues of De-Globalization
- Our Filipino Kind of Religion
- Our Filipino Christianity and Our God-concept
- When Our Religion Becomes Evil
THE RECTO READER is presented in several postings. Click each to open/read:
- THE RECTO READER: Nationalism,Internationalism,Ultra-Nationalism, Part 1A of 6
- THE RECTO READER: Mission of Nationalism, Part 1B of 6
- THE RECTO READER: Economic Independence,Economic Nationalism,Part 2A of 6
- THE RECTO READER: Economic Nationalism Means Industrialization,Part 2B of 6
- THE RECTO READER: Industrialization: The Alternative to Poverty, Part 2C of 6
- THE RECTO READER: The Fallacy of "Philippines First," Part 2D of 6
- THE RECTO READER: Parity Rights, Currency Dependence, Foreign Loans versus Foreign Investments, Part 2E of 6
NOTE: Recto's cited cases, examples or issues were of his time, of course; but realities in our homeland in the present and the foreseeable future are/expectedly much, much worse. Though I am tempted to update them with current issues, it's best to leave them as they are since Recto's paradigms about our much deepened national predicament still ring relevant, valid and true. In short, Recto saw the forest and never got lost in the trees.- Bert
- THE FILIPINO MIND blog contains 532 published postings you can view, as of December 12, 2012.
- The postings are oftentimes long and a few readers have claimed being "burnt out." My apologies. The selected topics are not for entertainment but to stimulate deep, serious thoughts per my MISSION Statement and hopefully to rock our boat of ignorance, apathy, complacency and hopefully lead to active citizenship.
- All comments are welcomed for posting at the bottom window. Comments sent by email will also be posted verbatim. However, ANONYMOUS COMMENTS WILL BE IGNORED.
- Visit my other website, click --> SCRIBD/TheFilipinoMind, or the SCRIB FEED at the sidebar, or type it on GOOGLE Search to read or download ebooks and PDFs of essays I have uploaded. Statistics for my associated website:SCRIBD/theFilipinoMind : ALL FREE AND DOWNLOADABLE: 123 documents, 207,458 reads
- Some postings and other relevant events are now featured in Google+, BMD_Facebook, BMD_Twitter and BMD_Google Buzz and Google+.
- Translate to your own language. Go to the sidebar and Click on GOOGLE TRANSLATOR (56 languages - copy and paste sentences, paragraphs and whole articles, Google translates a whole posting in seconds, including to Filipino!!).
- Forwarding the posts to relatives and friends, ESPECIALLY in the homeland, is greatly appreciated. Use emails, Twitter, Google+, Facebook, etc. THANK YOU !!!
- Songs on Filipino nationalism: please reflect on the lyrics (messages) as well as the beautiful renditions. Other Filipino Music links at blog sidebar. Click each to play.: